How Do You Find B
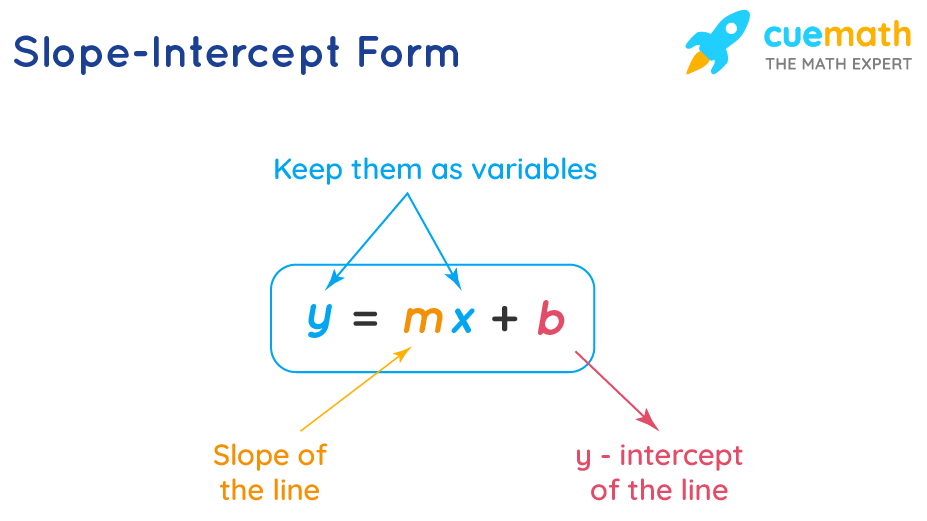
y=mx+b
y = mx + b is the slope intercept form of writing the equation of a straight line. In the equation 'y = mx + b', 'b' is the point, where the line intersects the 'y axis' and 'yard' denotes the gradient of the line. The slope or gradient of a line describes how steep a line is. It can take either a positive or a negative value. When a standard form of a linear equation is of the course Ax + By = C, where 'x' and 'y' and 'C' are variables and 'A', 'B' are constants, the slope-intercept form is the well-nigh preferred fashion of expressing a directly line due to its simplicity, as it is very easy to find the slope and the 'y intercept' from the given equation.
| one. | Pregnant of y = mx + b |
| 2. | How to Observe y = mx + b? |
| three. | Writing an Equation in the Gradient Intercept Form |
| iv. | Solved Examples on y mx b |
| 5. | Practice Questions on y mx b |
| 6. | FAQs on y mx b |
Meaning of y = mx + b
y = mx + b is the slope-intercept form of a staight line. In the equation y = mx + b for a straight line, m is chosen the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept of a line. y = mx+b, where
y ⇒ how far up or downwardly is the line,
ten ⇒ how far along is the line,
b ⇒ the value of y when x = 0 and
one thousand ⇒ how steep the line is.
This is determined by chiliad = (divergence in y coordinates)/ (difference in x coordinates). Notation that departure in y coordinates is indicated as rise or fall and deviation in 10 coordinates is indicated as run.
How To Find y = mx + b?
y = mx + b is the formula used to notice the equation of a straight line, when we know the slope(one thousand) and the y-intercept (b) of the line. To decide m, we use a formula based on the calculations. Let's derive this formula using the equation for the slope of a line. Let us consider a line whose slope is 'm' and whose y-intercept is 'b'. Let (x,y) exist any other random bespeak on the line whose coordinates are not known. We obtain the graph equally follows.

We know that the equation for the gradient of a line in the slope-intercept course is y = mx+b
Rewriting this, we become m = (y-b) / 10
Thus the formula to discover grand = change in y/ change in x
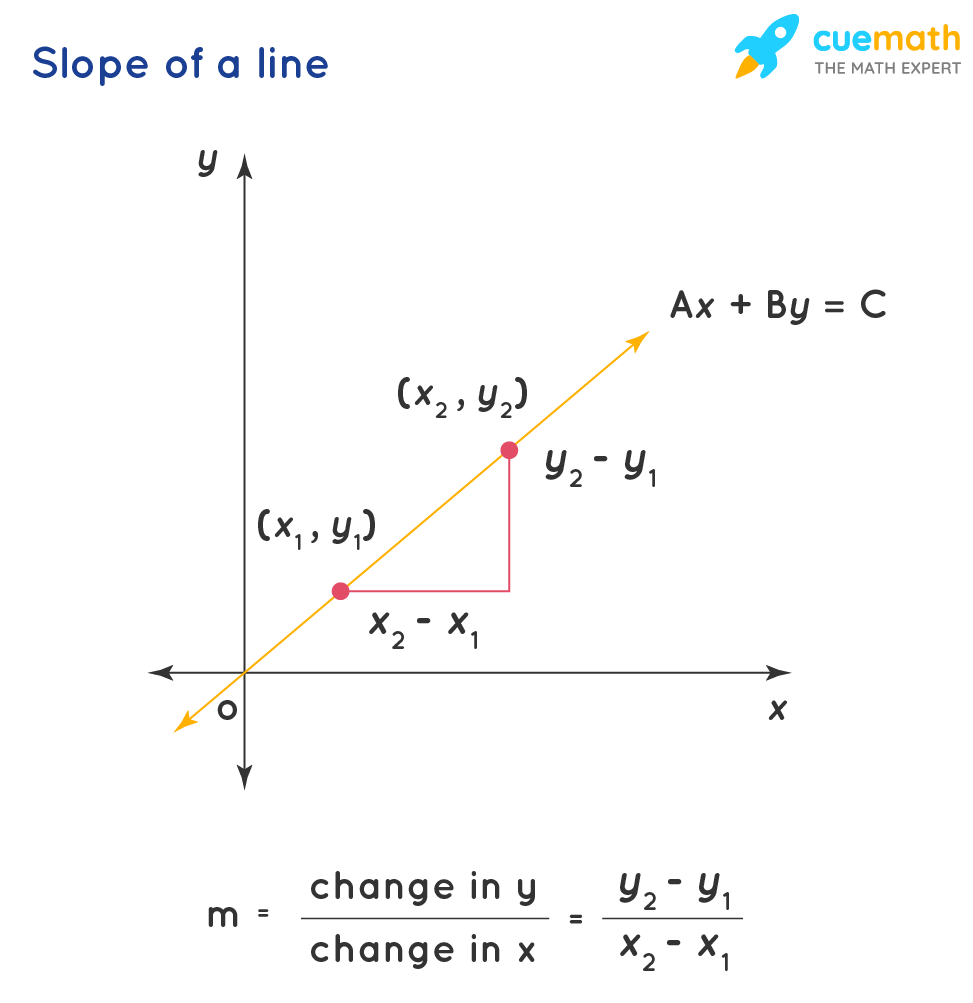
Let u.s. derive the formula to find the value of the slope if 2 points \((x_{i},y_{1})\) and \((x_{2},y_{2})\) on the directly line are known. Then we take \(y_{1} = mx_{1} + b\) and \(y_{ii} = mx_{2} + b\)
We know that, gradient = change in y/ change in ten
Substituting the values of y1 and y2, we get \[\brainstorm{align}\dfrac{y_{two}-y_{i}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}&= \dfrac{(mx_{ii}+b) - (mx_{1}+b)}{x_{two}-x_{ane}}\\\\&=\dfrac{mx_{2}-mx_{i}}{x_{2}-x_{one}}\\\\&= \dfrac{m(x_{ii}-x_{one})}{x_{2}-x_{one}}\\\\ &=m\stop{marshal}\]
Thus we find that the slope (thousand) is calculated as (change in y)/ (change in x)
thou = (divergence in y coordinates)/ (departure in x coordinates)
To observe the y-intercept or 'b', substitute the value of 'x' as 0 in the equation of a straight line, which is of the form Ax + Past + C = 0. Consider an equation of a straight line : 3x + 5y = 10. To discover the y-intercept, substitute the value of 'x' as 0 in the equation and solve for 'y'. On substituting 'x = 0' in the equation 3x + 5y =ten, nosotros go, three(0) + 5y = x
⇒5y = 10 and thus y = x/5 ⇒ y = ii or 'b' = 2.
Writing an Equation in The Gradient Intercept Form
If the slope 'thousand' and y-intercept 'b' are given, and then the equation of the straight line tin can be written in the form of 'y = mx +b'. For example, if the slope(m) for a line is 2 and the y-intercept 'b' is -i, then the equation of the directly line is written as y = 2x - 1. The slope value tin be positive or negative. As nosotros discussed in the earlier sections, in y = mx + b, 'm' represents the slope of the equation. To find the slope of a line, given its equation, we have to rearrange its terms to the slope-intercept form y = mx + b. Here, 'yard' gives the slope and 'b' gives the y-intercept of the equation.
Permit united states consider the equation 2x + 3y = 6. We are required to find the slope and the y-intercept from the equation which is of the form Ax + By = C
We rewrite the standard form of the equation of the line to the slope-intercept course y = mx + b.
2x + 3y = 6
3y = 2x + 6
y = (-2/iii) x + two
Comparison the last equation with y = mx + b, we obtain the slope of the equation is one thousand = -2/3 and the y-intercept of the equation is, b = 2 or (0,ii).
Important Notes:
- The equation of the slope-intercept form of a line whose gradient is 'yard' and whose y-intercept is 'b' or (0,b) is y = mx + b.
- The equation of a horizontal line passing through (a,b) is of the form y = b.
- The equation of a vertical line passing through (a,b) is of the form 10 = a.
- m is calculated using the formula rise over run or (change in y)/ (change in ten)
Topics Related to y = mx + b
Check out some interesting manufactures related to y = mx + b.
- Linear Equation Formula
- Equation of a Straight Line
- Linear Equations
- Linear Equations and Half Planes
- Point-slope formula
- Ii Point Form
-
Example 1: Observe the equation of the line whose graph contains the points (ane,3) and (three,7)
Solution:
The required equation of the line is y = mx + b
Using the formula for slope, grand = change in y / change in 10 = \(\dfrac{y_{2}-y_{ane}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}\)
= (7-three)/ (3-1) = 4/two ⇒ k = ii
To notice the y-intercept b, we consider any one of the coordinates.
Allow us use(1,3) and thou = 2 and substitute the values in the equation \(y_{1} = mx_{i} + b\)
iii = 2(1) + b ⇒ b = three - 2 = ane
Applying, grand =two and b = ane in the equation of the line(y = mx + b), we get y = 2x + ane Thus the equation of the straight line is y = 2x + 1 -
Example 2: Discover the gradient-intercept form of a line with slope -2 and which passes through the point (-1.4).
Solution:
We know that the slope-intercept class of a line is y = mx + b.
It is given that slope (1000) = -2 and the coordinates through which the line is passing through is (-1,4). Substituting the given values in the gradient-intercept form equation we get, 4 = (-2) (-one) + b.
iv = ii + b b = 4 - 2 = 2.
The slope intercept class of the line is y = - ii x + 2.
go to slidego to slide

Accept questions on basic mathematical concepts?
Become a problem-solving champ using logic, not rules. Learn the why backside math with our certified experts
Book a Free Trial Grade
FAQs on y mx b
What is y = mx + b?
y = mx + b is a representation of equation of a straight line. It is chosen as the slope intercept form. 'thousand' is referred to equally the slope of the line, and 'b' refers to the 'y -intercept' of the line.
How to Find the Gradient of a Line?
For two coordinates, (ten1,y1) and (x2, y2), the slope of a line is the ratio of difference between the difference betwixt the y coordinates and the divergence between x coordinates, besides known as the ascent over the run. The formula to find the slope of a line is one thousand = (y2-y1)/(x2-xi)
What is Slope-Intercept Form?
The equation of a straight line which is of the form y = mx + b, is called the slope intercept course. Here 'one thousand' is the slope of the line and 'b' is the indicate at which the line intercepts the y - axis. An instance for slope intercept form equation is y = 3x + v
What is a Line With a Negative Slope?
A line for which the slope in negative is said to move from left to right in a graph. The slope of a line is found by the ration of divergence in y-coordinates to the deviation in x-coordinates. If this value is negative for a line, then the line has a negative gradient.
What Does the Slope of a Line Hateful?
The direction of a line is described by its slope. The gradient tin be positive or negative, based on its direction. A negative slope moves downwardly from left to correct and a line with positive gradient moves in the upwardly direction from right to left.
How Do You Find B,
Source: https://www.cuemath.com/geometry/y-mx-b/
Posted by: walkerdeboyfaing.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Do You Find B"
Post a Comment